NEC Corporation has announced the development of the world’s first high-sensitivity uncooled infrared image sensor using high-purity semiconducting carbon nanotubes (CNTs). The groundbreaking technology is expected to have practical applications by 2025.
Infrared image sensors detect infrared rays emitted by people and objects, even in the dark. This makes them essential for various applications, including night vision for vehicles, aircraft navigation support systems, and security cameras. There are two types of sensors: cooled, which operates at extremely low temperatures, and uncooled, which operates near room temperature.
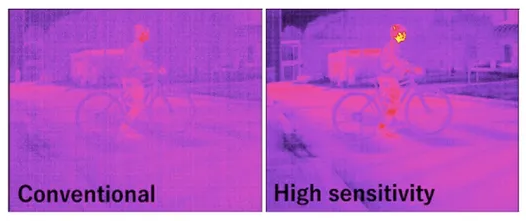
Cooled sensors are highly sensitive but require expensive, large, and energy-consuming coolers. Uncooled sensors, though more compact and affordable, have lower sensitivity and resolution. NEC’s new sensor overcomes these limitations, offering more than three times the sensitivity of mainstream uncooled sensors using vanadium oxide or amorphous silicon.
NEC, a pioneer in CNT research since 1991, developed a proprietary technology to extract only semiconducting-type CNTs at high purity in 2018. The company discovered that thin films of semiconducting-type CNTs exhibit a large temperature coefficient of resistance (TCR) near room temperature, which is crucial for high sensitivity.
The new sensor combines the thermal separation structure used in uncooled infrared image sensors, Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS) device technology, and NEC’s CNT printing and manufacturing technology. This has enabled the operation of a high-definition uncooled infrared image sensor with 640 x 480 pixels.
The development was partially achieved in collaboration with Japan’s National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) and supported by a security technology research promotion program conducted by Japan’s Acquisition, Technology & Logistics Agency (ATLA).
NEC will continue to develop and improve infrared image sensor technologies, aiming to contribute to various fields and areas of society with innovative products and services.


No comments yet.